Google has announced a series of new AI and accessibility features for Android and Chrome to improve the user experience, particularly for people with disabilities. A key update is the integration of Google’s Gemini AI into TalkBack, Android’s screen reader, which now allows users to ask questions about what’s on their screen and in images. This new feature provides more detailed descriptions, such as answering questions about an image of a guitar or the content on a shopping app, making it easier for people who are blind or have low vision to navigate their devices.
Alongside this update, Google has enhanced its Expressive Captions feature, which provides real-time captions with an added layer of expression. This update helps users understand how something is said, not just what is said. For instance, it now captures the duration of sounds, so you can hear a sports commentator saying “amaaazing shot” or someone stretching out their “no” as “nooooo”. Additionally, the captions will now include new labels for sounds like whistling or throat clearing, further enhancing the accessibility of spoken content.

Google has also made significant strides in improving the accessibility of PDFs on Chrome. Previously, screen readers couldn’t interact with scanned PDFs in the desktop browser, but now, thanks to Optical Character Recognition (OCR), Chrome can automatically recognise and allow users to highlight, copy, and search for text in scanned PDFs, making them more accessible. This update helps those relying on screen readers interact with content that was previously difficult to access.
Chrome for Android has also received an update that includes a new Page Zoom feature. This allows users to adjust the size of the text on webpages without disrupting the layout of the page itself. Users can now zoom in as needed and even set a default zoom preference for all pages or specific ones. This small but significant change enhances readability for people who need larger text while maintaining the overall integrity of webpage layouts.
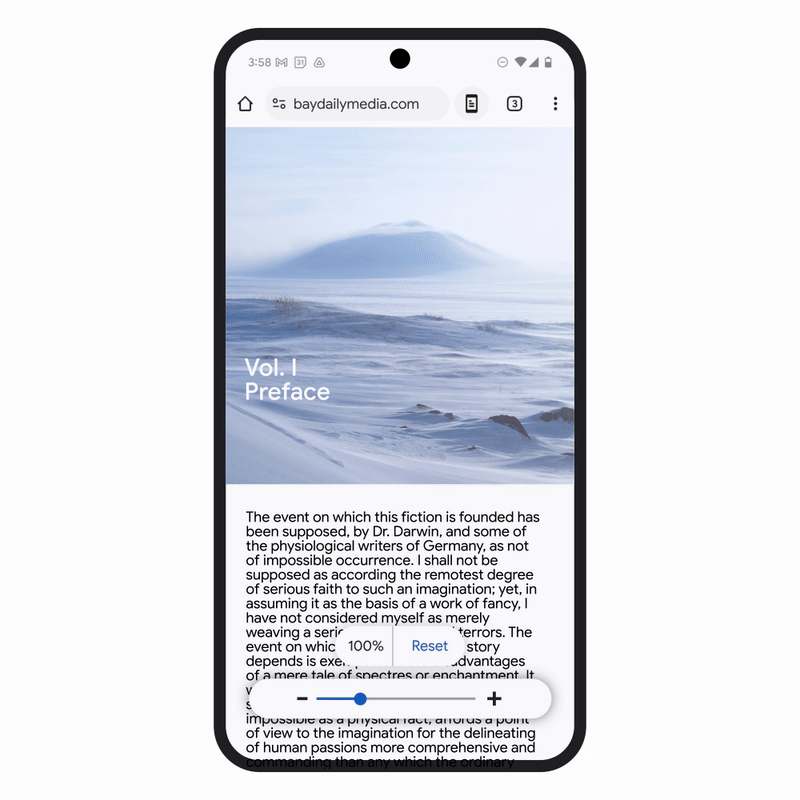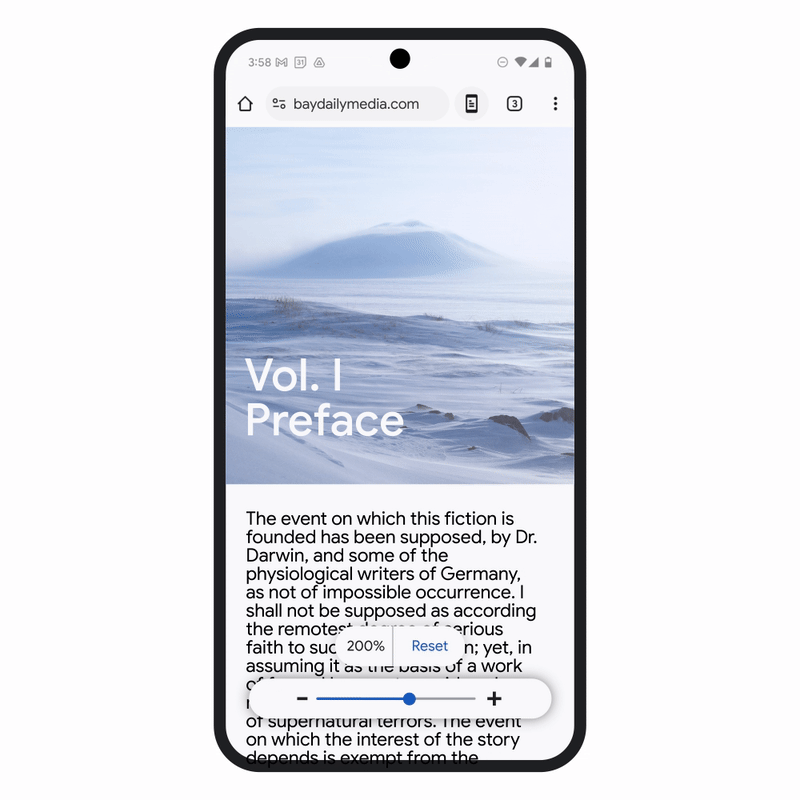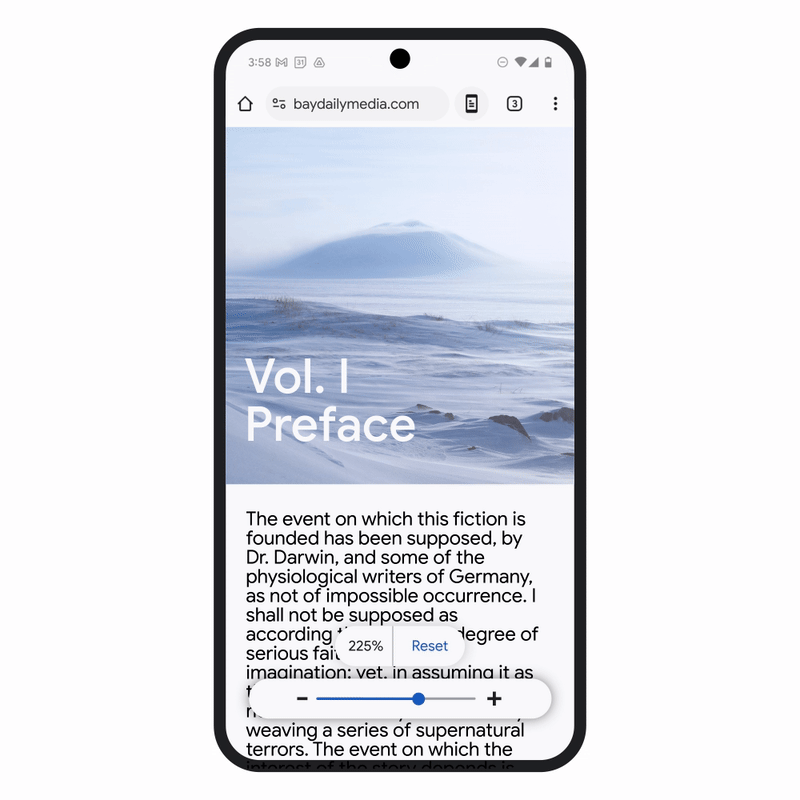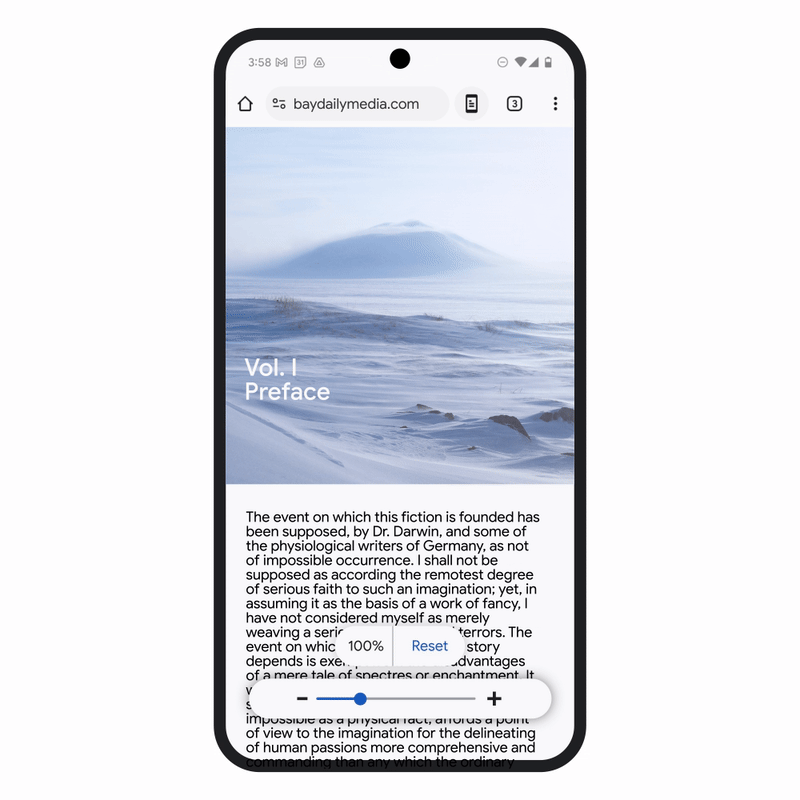
These updates represent Google’s ongoing commitment to making their platforms more inclusive, ensuring that accessibility is built into the core of their products. By integrating AI to enhance the functionality of existing features, Google is improving the experience for users across the globe, including those with visual impairments or other disabilities.
📲 Get the latest Tech & Startup News on our WhatsApp Channel
👉 Join Now



